cy.each examples
Confirm each item
Let's say we have a list of items
<ul>
<li class="fruit">Apples $10</li>
<li class="fruit">Bananas $20</li>
<li class="fruit">Grapes $15</li>
</ul>
Let's confirm each item starts with the fruit name
cy.get('li').each(($li) => {
// you can use Chai-jQuery assertions
expect($li.text()).to.match(/^(Apples|Bananas|Grapes)/)
expect($li).to.have.class('fruit')
// you can also use cy.wrap($li) to be able to use Cypress commands
cy.wrap($li)
.should('have.class', 'fruit')
.invoke('text')
.should('match', /\$\d+$/) // ends with a price
})
Non-dom values
cy.each can iterate over any items from a list / jQuery object
function isEven(n) {
return n % 2 === 0
}
cy.wrap([4, 6, 8, 10]).each((n) =>
expect(n, 'odd').to.satisfy(isEven),
)
Assert attributes
Let's confirm that every image has attribute alt with a non-empty value to be accessible.
📺 Watch this example explained in the video Check Each Image To Have An Alt Attribute.
<img
id="img1"
src="https://glebbahmutov.com/images/warming-stripes.png"
width="400"
height="50"
alt="Warming stripes first image"
/>
<br /><br />
<img
id="img2"
src="https://glebbahmutov.com/images/warming-stripes.png"
width="400"
height="50"
alt="Warming stripes second image"
/>
cy.get('img').each(($img, k) => {
expect($img, `image ${k + 1}`).to.have.attr('alt').to.not.be
.empty
})
Note: you could find all images without an alt attribute using a selector
cy.get('img:not([alt])').should('not.exist')
You can also find all images with an empty alt attribute
cy.get('img[alt=""]').should('not.exist')
Confirm prices
Let's say we have a list of prices. We need to confirm that every price is higher than $1.99
<ul>
<li class="price">$10</li>
<li class="price">$2.50</li>
<li class="price">$4.66</li>
<li class="price">$2.02</li>
</ul>
// first, confirm we have our prices
cy.get('.price')
.should('have.length.greaterThan', 2)
.each(($price, k) => {
// get the text from the jQuery element
const priceText = $price.text().trim()
// strip '$' and convert to a number
const price = Number(priceText.replace(/\$/g, ''))
// confirm the price is above the min price
expect(price, `item ${k + 1}`).to.be.above(2.0)
})
Collect items text
Let's say we have a list of items
<ul>
<li>Apples</li>
<li>Bananas</li>
<li>Grapes</li>
</ul>
Let's put all list items into a list and check it.
const list = []
cy.get('li')
.each(($li) => {
list.push($li.text())
})
.then(() => {
// by the time ".each" is finished
// the list is populated
expect(list).to.deep.equal(['Apples', 'Bananas', 'Grapes'])
})
Count items with matching text
If we have a list of items and want to count how many times the word "Apples" is in it
<ul>
<li>Apples</li>
<li>Bananas</li>
<li>Grapes</li>
<li>Apples</li>
<li>Apples</li>
<li>Kiwi</li>
</ul>
We should keep the count variable outside the .each callback and use .then to compare it to the expected value.
let count = 0
cy.get('li')
.each(($li) => {
if ($li.text() === 'Apples') {
count += 1
}
})
.then(() => {
// by the time ".each" is finished, the count has been updated
expect(count, 'Apples count').to.equal(3)
})
We can also use the built-in jQuery :contains(text) selector
cy.get('li:contains("Apples")').should('have.length', 3)
Stop cy.each iteration
The original issue #8652
Let's take the list of fruits again
<ul>
<li>Apples</li>
<li>Bananas</li>
<li>Grapes</li>
</ul>
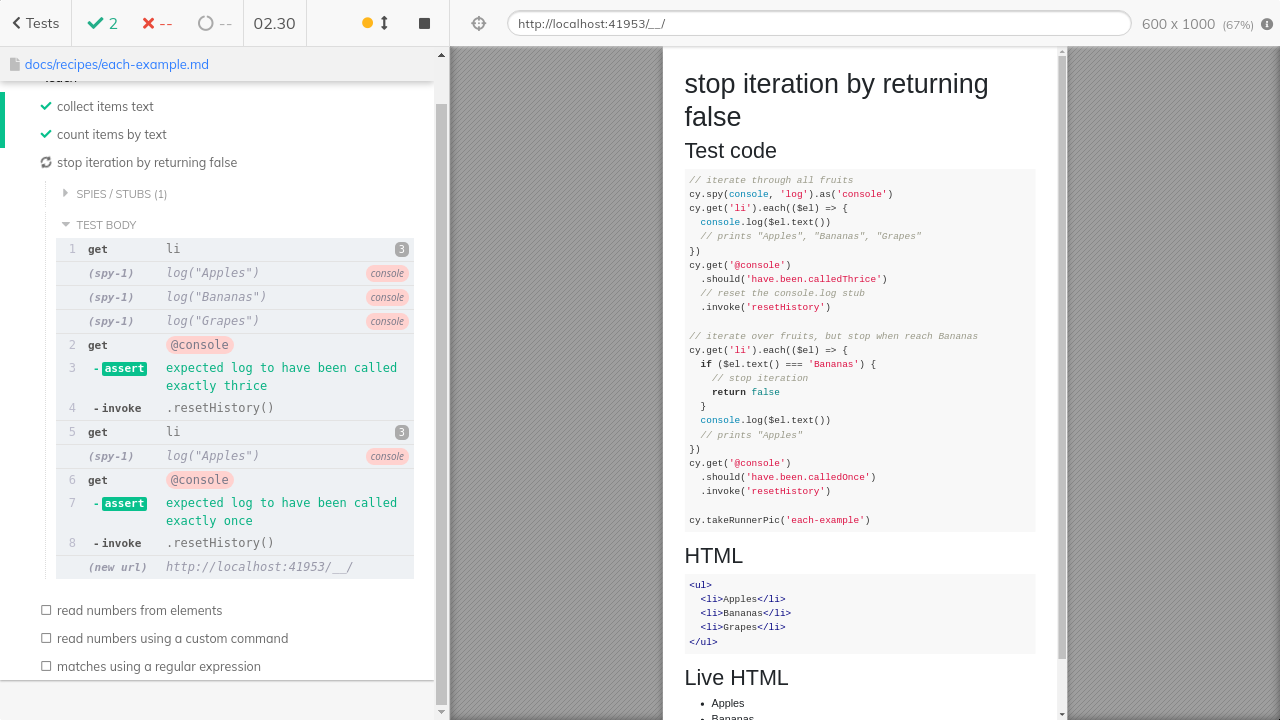
Let's print each item and then check that we have called console.log three times.
// iterate through all fruits
cy.spy(console, 'log').as('console')
cy.get('li').each(($el) => {
console.log($el.text())
// prints "Apples", "Bananas", "Grapes"
})
cy.get('@console')
.should('have.been.calledThrice')
// reset the console.log stub
.invoke('resetHistory')
// iterate over fruits, but stop when reach Bananas
cy.get('li').each(($el) => {
if ($el.text() === 'Bananas') {
// stop iteration
return false
}
console.log($el.text())
// prints "Apples"
})
cy.get('@console')
.should('have.been.calledOnce')
.invoke('resetHistory')
cy.takeRunnerPic('each-example.png')
Early stop does not change the subject
Even if you stop the iteration early by returning false, the original subject is still passed to the next command or assertion.
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
cy.wrap(numbers)
.each((number) => {
// stop the iteration when we get to the number 2
return number === 2 ? false : true
})
// the same original array is still passed
// to the next assertion
.should('equal', numbers)
How to read values from elements using .each?
<ul>
<li>10</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
</ul>
const list = []
cy.get('li')
.each(($li) => {
list.push(parseInt($li.text()))
})
// by the time ".each" is finished
// the list should have 3 numbers, let's grab it
.wrap(list)
.should('deep.equal', [10, 5, 6])
<ul>
<li>10</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
</ul>
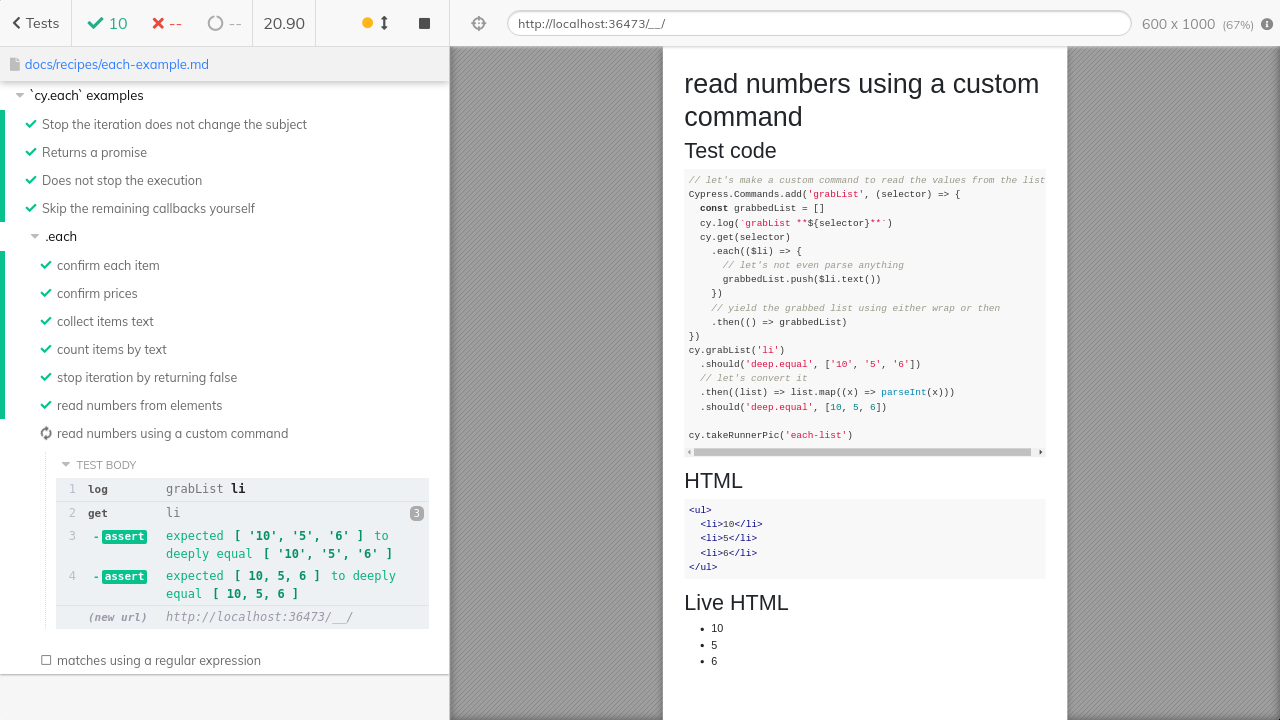
alternative: using a custom command
// let's make a custom command to read the values from the list
Cypress.Commands.add('grabList', (selector) => {
const grabbedList = []
cy.log(`grabList **${selector}**`)
cy.get(selector)
.each(($li) => {
// let's not even parse anything
grabbedList.push($li.text())
})
// yield the grabbed list using either wrap or then
.then(() => grabbedList)
})
cy.grabList('li')
.should('deep.equal', ['10', '5', '6'])
// let's convert it
.then((list) => list.map((x) => parseInt(x)))
.should('deep.equal', [10, 5, 6])
cy.takeRunnerPic('each-list')
Note: you can also use cy.map or cy.mapChain commands from my cypress-map plugin to implement this test and collect information from each element.
Match regular expression with OR
Imagine we have a lit of prices, and each item can have a dollar amount or "Pay As You Want" string. Let's confirm this.
<ul>
<li>
<span class="item">Apples</span>
<span class="price">$0.99</span>
</li>
<li>
<span class="item">Grapes</span>
<span class="price">Pay As You Want</span>
</li>
<li>
<span class="item">Tomatoes</span>
<span class="price">$2.69</span>
</li>
<li>
<span class="item">Lemons</span>
<span class="price">Pay as you want</span>
</li>
</ul>
<style>
.price {
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
// first ensure the number of prices is the same as items
cy.get('.item')
.should('have.length.gt', 0)
.its('length')
.then((n) => {
cy.get('.price').should('have.length', n)
})
// cy.each callback receives the jQuery element
cy.get('.price').each(($price, k) => {
const text = $price.text()
// find out the item name for better messaging
const item = $price.parent().find('.item').text()
// our regular expression should match prices
// and the "pay as you go text" and ignore case
const expression = /^(\$\d+\.\d\d|pay as you want)$/i
expect(text, `${k + 1}: ${item}`).to.match(expression)
})
See also Collect Headings recipe.
.each callback can return a promise
You can return a promise from each(callback). Cypress will wait for the promise to resolve before continuing.
let lastSeen = 0
cy.wrap([1, 2, 3, 4])
.each((number) => {
lastSeen = number
// the returned promise delays each command by 1 second
// NOTE: it does not change the yielded value,
// the original value is yielded to the next command or assertion
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(number * 2)
}, 1000)
})
})
.should('be.an', 'array')
// the original array is unchanged
.should('deep.equal', [1, 2, 3, 4])
.then(() => {
// cy.each went through all numbers
expect(lastSeen).to.equal(4)
})
Cannot stop the iteration when using a Promise
If you delay the execution by returning a Promise from cy.each(callback), its resolved value is ignored, and it does not stop the execution early.
let lastSeen = 0
cy.wrap([1, 2, 3, 4])
.each((number) => {
lastSeen = number
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// try to stop early by resolved with false
resolve(number === 2 ? false : true)
}, 1000)
})
})
.should('be.an', 'array')
// the original array is unchanged
.should('deep.equal', [1, 2, 3, 4])
.then(() => {
// cy.each still went through all numbers
expect(lastSeen).to.equal(4)
})
Skip the remaining callbacks yourself
For more complicated behavior, use an outside variable to signal when to skip the remaining items and stop the iteration using cy.then and the variable check.
<table id="lotto">
<thead>
<th>Pick This</th>
<th>Number</th>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button>Click me</button></td>
<td>???</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<script>
document
.querySelector('table tbody')
.addEventListener('click', function (event) {
if (event.target.nodeName === 'BUTTON') {
// set the text in the next cell, but after async delay
// to make sure we write a flake-free test that retries
setTimeout(function () {
const cell =
event.target.parentElement.parentElement.children[1]
cell.innerText = Math.random().toString().substr(2, 1)
}, 1000)
}
})
</script>
In the above table, each click on the button reveals the number in the cell next to it. Let's iterate over the buttons until we click a button and it reveals the lucky number "7". The cy.each callback is called immediately with N elements, queueing up the commands inside the callback. By using cy.then plus if (stopIteration) { return } combination we can iterate over the elements, perform Cypress commands and stop early.
// this variable will be checked and set inside the `.each(callback)`
let stopIteration = false
// grab all buttons from the table
cy.get('#lotto tbody tr button')
.should('have.length.greaterThan', 10)
.each(($button, k) => {
// schedule N cy.then commands right away
cy.then(() => {
// if some previous iteration found the number 7
// no longer perform any more button clicks
if (stopIteration) {
return
}
// from the jQuery element, start a new Cypress command chain
cy.wrap($button, { log: false })
.click()
// once the button is clicked,
// find the text in the cell next to it
.parent() // <TD>
.parent() // <TR>
.find('td')
.eq(1) // <TD> with the number
.should(($td) => {
// check if the revealed number is 7
const text = $td.text()
expect(text).to.match(/\d/)
if (text === '7') {
// tell the next iterations of cy.each(callback)
// to return early
stopIteration = true
}
})
})
})
Separate Zip codes
Let's imagine that we are writing a delivery application. We might deliver to some zip codes, but not to others. Our application has the list of valid zip codes, and allows us to check if a given zip code is valid or not.
<input id="zip" placeholder="Enter zip code to check" />
<div>
Is zip code <span id="entered"></span> supported?
<span id="supported"></span>
</div>
<script>
const supported = ['90210', '80810']
const supportedEl = document.getElementById('supported')
const enteredEl = document.getElementById('entered')
const zipEl = document.getElementById('zip')
zipEl.addEventListener('focus', (e) => {
supportedEl.innerText = ''
})
zipEl.addEventListener('change', (e) => {
const zip = e.target.value
enteredEl.innerText = zip
e.target.value = ''
supportedEl.innerText = '...'
// use a small delay before showing the result
setTimeout(() => {
if (supported.includes(zip)) {
supportedEl.innerText = '✅'
} else {
supportedEl.innerText = '👎'
}
}, 1000)
})
</script>
const allZips = ['90210', '55555', '02123', '80810']
// list of zip codes the application delivers to
const delivers = []
// list of zip codes the application does not support
const invalid = []
cy.wrap(allZips).each((zip) => {
cy.get('#zip').type(zip + '{enter}')
cy.get('#supported')
.invoke('text')
.should('be.oneOf', ['✅', '👎'])
.then((supported) => {
if (supported === '✅') {
delivers.push(zip)
} else {
invalid.push(zip)
}
})
// sleep for one second for clarity
.wait(1000, { log: false })
})
Now that the above code checked the zip codes using the application, let's confirm the lists are correct.
cy.log('**delivers to**')
cy.wrap(delivers).should('deep.equal', ['90210', '80810'])
cy.log('**maybe in the future**')
// we use .then callback because the list "delivers"
// only is computed by the previous commands, thus it will
// be filled by the time the .then(callback) runs
.then(() => {
const unsupported = Cypress._.difference(allZips, delivers)
cy.wrap(invalid).should('deep.equal', unsupported)
})
Watch the video Check The List Of Zip Codes.