Cypress API
Examples of uses of the Cypress API, for a full reference, go to docs.cypress.io
Cypress.Commands.add()
To add a command, use Cypress.Commands.add().
Cypress.Commands.add(
'console',
{
prevSubject: true,
},
(subject, method) => {
method = method || 'log'
// log the subject to the console
console[method]('The subject is', subject)
return subject
},
)
// prints the object to the window console
cy.wrap({ life: 42 }).console('info')
To yield a value from a custom command to the next command or assertion
Cypress.Commands.add(
'double',
{
prevSubject: true,
},
(value, method) => {
return value * 2
},
)
cy.wrap(21).double().should('equal', 42)
You can also wrap a value to be returned - Cypress automatically takes the value of the last command.
Cypress.Commands.add(
'triple',
{
prevSubject: true,
},
(value, method) => {
cy.wrap(value * 3)
},
)
cy.wrap(21).triple().should('equal', 63)
Note: you cannot both use cy.wrap and return in the same code, since it is ambiguous, watch the video Fix The Cypress Error "You are mixing async and sync code".
You can control how logging is done inside the custom command. You can even have a custom command with multiple DOM snapshots.
Calling other custom commands
You can call other custom commands from inside a custom command.
Cypress.Commands.add('name', () => 'Joe')
Cypress.Commands.add('greeting', () =>
// call the custom command cy.name
// then form the full greeting text and yield it
cy.name().then((n) => `Hello, ${n}`),
)
cy.greeting().should('equal', 'Hello, Joe')
Cypress.Commands.overwrite()
You can overwrite an existing Cypress command, either completely replacing it or wrapping with extra code. For example, to always repeat the string when typing, let's overwrite the cy.type command:
<input id="type-here" />
Cypress.Commands.overwrite('type', function (type, $el, text) {
// call the original "type" command twice on the jQuery element
return type($el, text + text)
})
cy.get('#type-here')
.type('Hello')
.should('have.value', 'HelloHello')
Rename and replace the cy.then command
See the recipe Replace cy.then command.
Cypress.Cookies.debug()
To enable or disable cookie debugging, use Cypress.Cookies.debug().
// Cypress will now log in the console when
// cookies are set or removed
Cypress.Cookies.debug(true)
cy.setCookie('fakeCookie', '123ABC')
cy.clearCookie('fakeCookie')
cy.setCookie('fakeCookie', '123ABC')
cy.clearCookie('fakeCookie')
cy.setCookie('fakeCookie', '123ABC')
Cypress.Cookies.preserveOnce() (deprecated)
Deprecated, use cypress-v10-preserve-cookie.
To preserve cookies by its key, use Cypress.Cookies.preserveOnce().
cy.getCookie('fakeCookie').should('not.be.ok')
// preserving a cookie will not clear it when
// the next test starts
cy.setCookie('lastCookie', '789XYZ')
Cypress.Cookies.preserveOnce('lastCookie')
Cypress.Cookies.default() (deprecated)
Deprecated, use cypress-v10-preserve-cookie.
To set defaults for all cookies, use Cypress.Cookies.default().
Cypress.Cookies.defaults({
preserve: 'session_id',
})
Cypress.Server.default() (deprecated)
To change the default configuration for cy.server, use Cypress.Server.defaults().
Cypress.Server.defaults({
delay: 0,
force404: true,
ignore: function (xhr) {
// handle custom logic for ignoring certain requests
},
})
Cypress.arch
To get CPU architecture name of underlying OS, use Cypress.arch.
// https://on.cypress.io/arch
expect(Cypress.arch).to.exist
Cypress.config()
To get or set configuration options, use Cypress.config(). Note: the config object should be reserved for Cypress settings, like baseUrl and viewportWidth. To store your custom values use the Cypress.env() approach.
const myConfig = Cypress.config()
// the config has a combination of default
// and user values from cypress.json file
expect(myConfig).to.have.property(
'animationDistanceThreshold',
5,
)
expect(myConfig).to.have.property('defaultCommandTimeout', 4000)
expect(myConfig).to.have.property('requestTimeout', 5000)
expect(myConfig).to.have.property('responseTimeout', 30000)
expect(myConfig).to.have.property('viewportHeight', 1000)
expect(myConfig)
.to.have.property('viewportWidth')
// previous assertion yields the value
// now let's assert the value pretending
// we only know min and max limits
.within(600, 1000)
expect(myConfig).to.have.property('pageLoadTimeout', 60000)
expect(myConfig).to.have.property('waitForAnimations', true)
// we can check if the property is present without checking its value
expect(myConfig).to.have.property('baseUrl')
// setting and getting an individual property
expect(Cypress.config('pageLoadTimeout')).to.eq(60000)
Cypress.config('pageLoadTimeout', 20000)
expect(Cypress.config('pageLoadTimeout')).to.eq(20000)
Cypress.config('pageLoadTimeout', 60000)
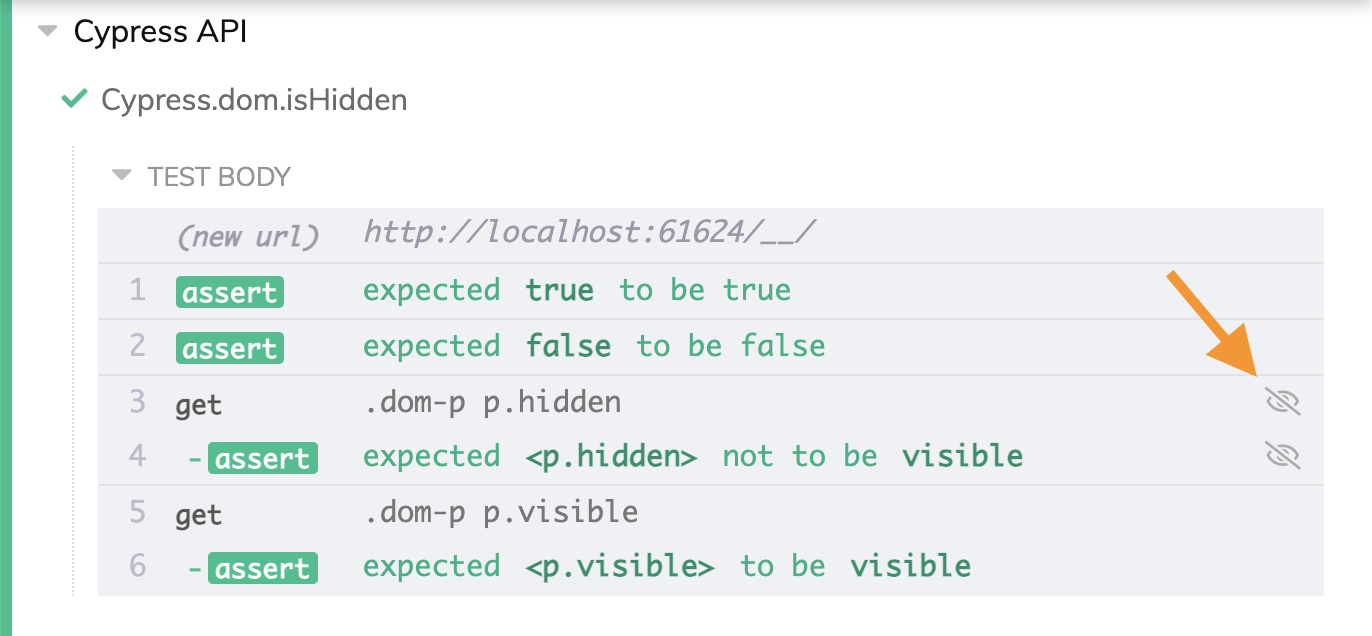
Cypress.dom.isHidden()
To see whether a DOM element is hidden, use Cypress.dom.isHidden().
<div class="dom-p">
<p class="hidden">I'm hiding!</p>
<p class="visible">I'm visible!</p>
</div>
let hiddenP = Cypress.$('.dom-p p.hidden').get(0)
let visibleP = Cypress.$('.dom-p p.visible').get(0)
// our first paragraph has css class 'hidden'
expect(Cypress.dom.isHidden(hiddenP)).to.be.true
expect(Cypress.dom.isHidden(visibleP)).to.be.false
Tip: elements that are hidden have a special "crossed eye" icon next to them in the Command Log.
cy.get('.dom-p p.hidden').should('not.be.visible')
cy.get('.dom-p p.visible').should('be.visible')
Cypress.env()
To get or set environment variable, use Cypress.env().
// set multiple environment variables
Cypress.env({
host: 'veronica.dev.local',
api_server: 'http://localhost:8888/v1/',
})
// get environment variable
expect(Cypress.env('host')).to.eq('veronica.dev.local')
// set environment variable
Cypress.env('api_server', 'http://localhost:8888/v2/')
expect(Cypress.env('api_server')).to.eq(
'http://localhost:8888/v2/',
)
// get all environment variable
expect(Cypress.env()).to.have.property(
'host',
'veronica.dev.local',
)
expect(Cypress.env()).to.have.property(
'api_server',
'http://localhost:8888/v2/',
)
Cypress.platform
To get name of underlying OS, use Cypress.platform.
// https://on.cypress.io/platform
expect(Cypress.platform).to.be.exist
Cypress.platform
To get name of underlying OS, use Cypress.platform.
// for example "darwin" on Mac
expect(Cypress.platform).to.exist
Cypress.version
To get version of Cypress being run, use Cypress.version.
// https://on.cypress.io/version
expect(Cypress.version).to.be.exist
Here is an example of parsing Cypress version and confirming it is at least v9. You can watch the explanation in the short video 📺 Parse Cypress Version String And Confirm The Major Version.
console.log(Cypress.version)
const [major, minor, patch] = Cypress.version
.split('.')
.map(Number)
console.log({ major, minor, patch })
expect(major, '>= v9 requires').to.be.gte(9)
Cypress.spec
Cypress.spec returns you the properties of the spec under test.
// https://on.cypress.io/spec
// wrap the object so we can inspect it easily by clicking in the command log
cy.wrap(Cypress.spec).should('include.keys', [
'name',
'relative',
'absolute',
])
Multiple specs
If you are using cypress open to run multiple specs at once, you can detect it by using the Cypress.spec object. The field name will be set to "All Integration Specs" and the fields absolute and relative will be set to "__all".
if (Cypress.spec.absolute === '__all') {
cy.log('Running several specs together')
} else {
cy.log(`Running a single spec ${Cypress.spec.relative}`)
}
Cypress.currentTest
Cypress.currentTest is an object representing the currently executing test instance, with properties to access the title of the test.
// https://on.cypress.io/currenttest
// wrap the object so we can inspect it easily by clicking in the command log
cy.wrap(Cypress.currentTest)
.should('include.keys', ['title', 'titlePath'])
.then((currentTest) => {
expect(currentTest).to.have.property(
'title',
'Get the current test information',
)
// get the entire full title, including the parent suite titles
expect(currentTest)
.to.have.property('titlePath')
.to.deep.equal([
'Cypress API', // the top suite
'Cypress.currentTest', // the parent suite
'Get the current test information', // the test title
])
})
Cypress.testingType
Cypress.testingType returns the current testing type, determined by the Test Runner chosen to run. The Cypress.testingType returns "e2e" for Cypress Test Runner integration tests, or "component" for experimental Component Testing.
expect(Cypress.testingType)
.to.be.oneOf(['e2e', 'component'])
// in this case, we are running e2e spec
.and.be.equal('e2e')